思路
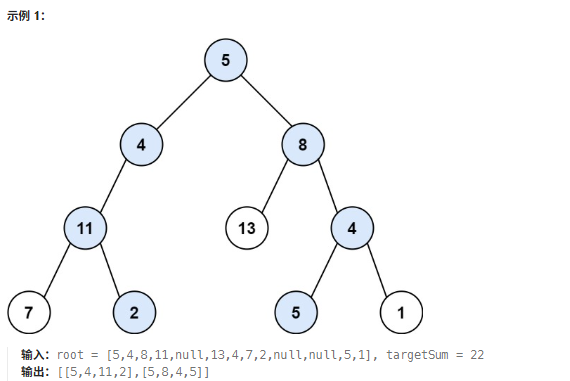
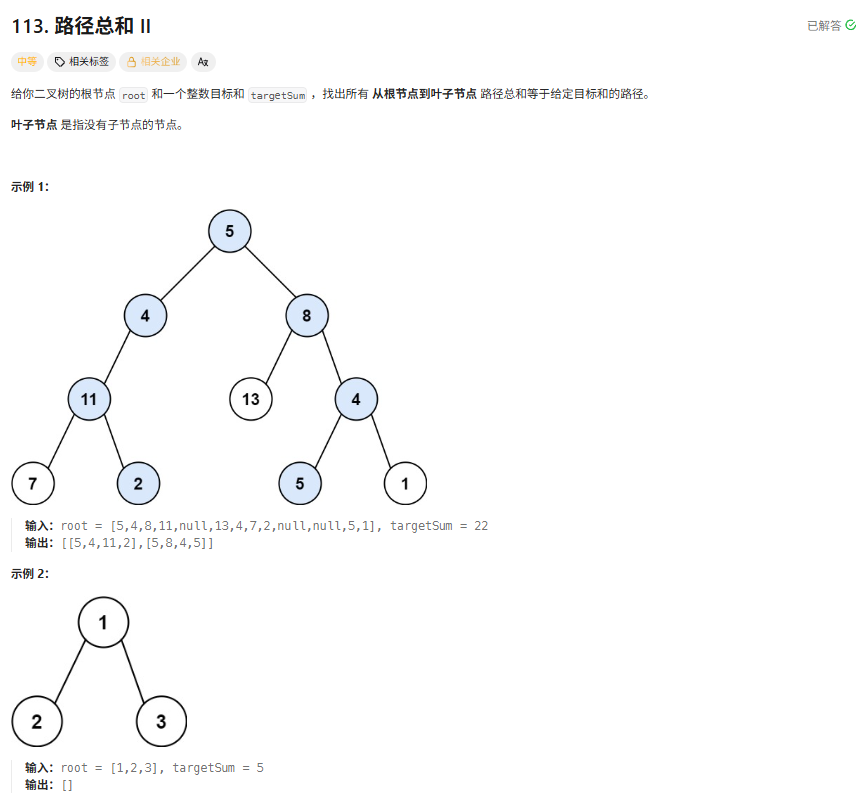
本题要求寻找所有从根节点到叶子节点,路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。 我们使用用深度优先搜索算法来搜索每一条路径,搜索完一条路径后回溯来搜索另一条路径。 可以在搜索到每一个节点的时候,用目标值减去当前节点的值得到新目标值,回溯的时候就可以用当前的目标值加上path数组最后一位的值,再将path数组最后一个值弹出。
方法
路径记录与目标值更新:每访问一个节点,将其加入path数组,目标值再减去当前节点值得到新目标值。
终止条件:若当前节点是叶子节点(左右子节点均为nullptr)且当前目标值为 0,说明找到一条有效路径,将其加入结果数组。
递归深入:当左子树或右子树存在时,用递归深入探索当前节点的左、右子树。
回溯:递归返回后,将当前节点从path数组中移除,并把path数组中最后一个数字加回目标值(撤销当前选择,避免影响其他路径的探索)。
复杂度
时间复杂度: O(N)
空间复杂度: O(N)
代码
下方为力扣提交代码,可以查看我的题解113. 路径总和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> path; //创建path数组,用于记录每一次搜索路径
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, vector<vector<int>>& sum) {
path.push_back(root->val); //将当前节点压入数组中
targetSum -= root->val; //目标值减去当前节点的值
//一条路径搜索的结束条件:剩余目标值为0并且是叶子节点
if (targetSum == 0 && root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
sum.push_back(path); //将当前路径加入总路径数组中
}
//只有当下一个目标节点存在时才进行递归
if (root->left != nullptr) dfs(root->left, targetSum, sum);
if (root->right != nullptr) dfs(root->right, targetSum, sum);
//回溯,当没搜索到路径或者找到一条路径后,回溯至上一步继续搜索
targetSum += path[path.size() - 1];
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> sum; //创建存储所有路径的结果数组
if (root != nullptr) dfs(root, targetSum, sum); //根节点存在时才进行搜索
return sum;
}
};下方为测试代码,包括建立二叉树等全部代码。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> path;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum, vector<vector<int>>& sum) {
path.push_back(root->val);
targetSum -= root->val;
if (targetSum == 0 && root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
sum.push_back(path);
}
if (root->left != nullptr) dfs(root->left, targetSum, sum);
if (root->right != nullptr) dfs(root->right, targetSum, sum);
targetSum += path[path.size() - 1];
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> sum;
if (root != nullptr) dfs(root, targetSum, sum);
return sum;
}
};
int main() {
TreeNode* tree = new TreeNode(5, new TreeNode(4, new TreeNode(11, new TreeNode(7), new TreeNode(2)), nullptr),
new TreeNode(8, new TreeNode(13), new TreeNode(4, new TreeNode(5), new TreeNode(1))));
TreeNode* tree2 = new TreeNode(1, new TreeNode(2), nullptr);
Solution s;
vector<vector<int>> sum = s.pathSum(tree, 22);
for (auto path : sum) {
for (auto val : path) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
sum = s.pathSum(tree2, 1);
for (auto path : sum) {
for (auto val : path) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出示例
5 4 11 2
5 8 4 5